The Biggest Routing Protocol in The World
in 2011 i created me and my earlier Manager Wahiduddin [TIKO] a group called [BGP For Life] 
and Implemented an over 10 BGP Site and reach to 30 Site in 2 year and i fell in love till VOIP Came and got engaged in it for a while, so i decide to create my BGP blogs.
i will walk you through my BGP Series how to configure BGP in every way i know ;D
We have 65535 number we choose from our AS just like private and public IP addresses:
- 0 : reserved.
- 1-64,495 : Public AS numbers.
- 64,496 – 64,511 : reserved to use in documentation.
- 64,512 – 65,534 : Private AS numbers use for customer and my LABs.
- 65,535 : reserved.
So BGP Resume:
- It use TCP-Based Port 179
- Triggered Update 5 Second Internally and 30 Second Externally
- Complicated “Metric” for finding the best route
- Neighbors Manually Configured
- BGP Packets (Open, Update, Keepalive & Notification)
- BGP Status (Idle, Active, Open Sent, Open Confirm & Established)
I will use GNS3 for my Labs so let start by configure basic connectivity between two router

i will start by configuring the interface for R1 and loopback 
Then proceed with R2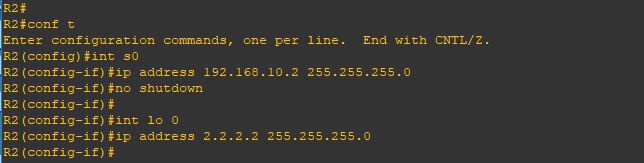
Now the BGP Neighbor Configuration on R1 by first mention the AS number of R1 (remote-as)
then the first command for our neighbor is by typing their IP Address of Router and their AS number
Repeat the same step on R2
Finally the neighbor came up
Same in Router 2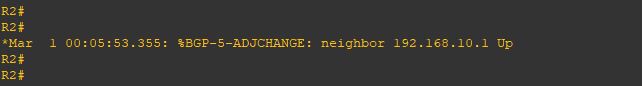
Now i will Issue the command (show ip bgp summary) which is a quick overview of your Border Gateway Protocol neighbor status, showing neighbor IPs, ASNs, BGP state (Idle, Connect, Established), uptime, and the number of prefixes learned/advertised, helping quickly spot peering issues or route exchange problems
repeat the same command on R2
Now i will tells a router to advertise specific IP prefixes to its BGP neighbors by issuing the command
(network x.x.x.x mask x.x.x.x)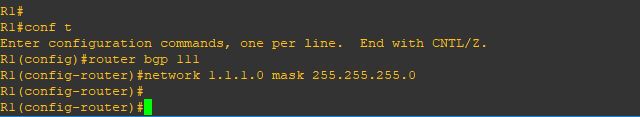
Repeat the same on R2
and now you can see the network that been advertise to you by issuing the command
(show ip bgp) and if you look at the local network on my router [1.1.1.0/24] have a weight of (32768)
which is local to me but the other network [2.2.2.0/24] have a path of an AS 222
Same on R2
test connectivity using [ping] and it goes very well
if you look above we advertise the network using (network x.x.x.x mask x.x.x.x) because unlike IGP protocols, it only injects routes that already exist as exact matches (network address and subnet mask) in the router’s local routing table. let me show you
i will configure the new loopback 1 with a /24 mask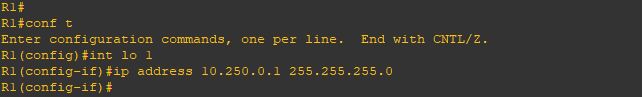
and advertise it without mentioning the Mask 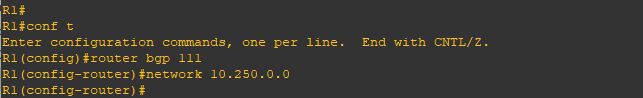
and as you can see it doesn’t show up because the BGP will advertise the default subnet mask for the network (10.0.0.0) which is (/8) and that subnet not available under my network 
so let’s correct it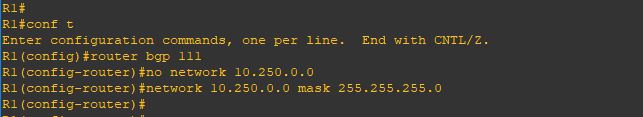
and Wallaaaaaaa
and yup i can ping it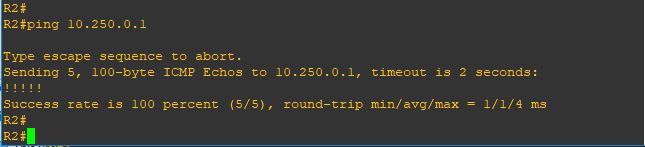
Note:
- IBGP administrative distance of 200 while EBGP is 20
- When your router learns about a prefix through EBGP and an IGP (RIP, OSPF or EIGRP) then it will always prefer the external BGP route. EBGP uses an administrative distance of 20 so it’s preferred over OSPF (110), RIP (120), or EIGRP (90).